Feed in Aquaculture
Feed is one of the crucial factors in determining the success of aquaculture. For example, in the context of shrimp farming, around 60-70% of the total operational costs are allocated to feed procurement. The choice of type and quality of feed must be done carefully, with the aim of stimulating optimal growth and development of shrimp. (Source: Biology Natural Resources Journal).
The types of feed that can be used can be natural feed and artificial feed. In terms of nutritional composition, artificial feed has been designed to provide nutrients including carbohydrates, protein, fat, fiber and a number of other important elements. However, not only aspects of nutritional composition are considered, but also the physical characteristics of the feed must meet the requirements needed to support optimal growth and development. These factors include the buoyancy and stability of feed in water (Saade and Aslamyah, 2009).
Why Test Stability In Water
Testing the stability of feed in water means testing the level of feed resistance in water, or how long it takes for the feed to soften and break down.
This test is very important because of the biological nature of shrimp which consume food slowly and continuously. Feed that is unstable and decomposes quickly in water can result in a decrease in water quality, causing conditions that are not supportive for the life and growth of shrimp (Naharuddin 2008)
The importance of testing feed stability in water is proven by the number of SNIs that apply this standard
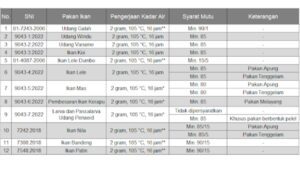
How SIG Helps
As an ISO 17025 accredited laboratory, SIG is now able to measure feed stability values in water, including breaking speed tests and solid dispersion tests according to applicable SNI.

